Overview:
In this short tutorial, I would like to show Redis Transaction with Spring Boot.
Redis Transaction:
A Database Transaction is a set of operations which is either executed successfully a single unit of work or the changes are discarded in case of issues.
Most of the redis commands can be grouped under get/set. All these commands are atomic by default. But when we need to execute a set of commands sequentially, then it is NOT guaranteed to be atomic. Redis provides a support for transaction through multi, exec and discard commands.

We first tell redis that we are going to run a set of operations by invoking multi command. Then we perform the operations (A, B and C) as usual as shown in the below picture. Once done, we either call exec() if things are good or discard() to ignore the changes.
Sample Application:
We are going to consider a simple Bank application in which Redis is the primary DB. We have set of accounts. The users can transfer money from 1 account to another.
Lets see how to implement the money transfer as Redis Transaction with Spring Boot.
Project Setup:
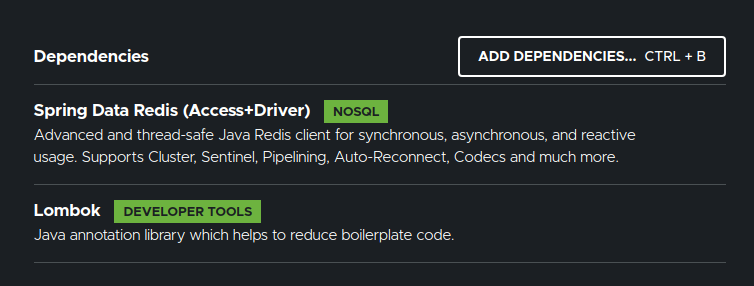
Create a Spring Boot project with below dependencies.
Account:
Lets create a simple Account class as shown here.
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
public class Account implements Serializable {
private int userId;
private int balance;
}Redis Transaction – SessionCallBack:
Spring Data Redis provides the SessionCallBack interface which needs to be implemented when we need to execute multiple operations as a single transaction.
- MoneyTransfer is an implementation of SessionCallBack which contains the business logic for money transfer.
- It will receive account Ids and the amount to be transferred.
@AllArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
public class MoneyTransfer implements SessionCallback<List<Object>> {
public static final String ACCOUNT = "account";
private final int fromAccountId;
private final int toAccountId;
private final int amount;
@Override
public <K, V> List<Object> execute(RedisOperations<K, V> redisOperations) throws DataAccessException {
var operations = (RedisTemplate<Object, Object>) redisOperations;
var hashOperations = operations.opsForHash();
var fromAccount = (Account) hashOperations.get(ACCOUNT, fromAccountId);
var toAccount = (Account) hashOperations.get(ACCOUNT, toAccountId);
if(Objects.nonNull(fromAccount) && Objects.nonNull(toAccount) && fromAccount.getBalance() >= amount){
try{
operations.multi();
fromAccount.setBalance(fromAccount.getBalance() - amount);
toAccount.setBalance(toAccount.getBalance() + amount);
hashOperations.put(ACCOUNT, fromAccountId, fromAccount);
hashOperations.put(ACCOUNT, toAccountId, toAccount);
return operations.exec();
}catch (Exception e){
operations.discard();
}
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}Demo:
That’s it. We could add some accounts into Redis and test the Redis Transaction.
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisTransactionApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisTransactionApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// initialize some accounts
this.redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(MoneyTransfer.ACCOUNT, 1, Account.of(1, 100));
this.redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(MoneyTransfer.ACCOUNT, 2, Account.of(2, 20));
// do the transaction
this.redisTemplate.execute(MoneyTransfer.of(1, 2, 30));
// print the result
System.out.println(this.redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(MoneyTransfer.ACCOUNT, 1));
System.out.println(this.redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(MoneyTransfer.ACCOUNT, 2));
}
}Output:
Account(userId=1, balance=70)
Account(userId=2, balance=50)Summary:
We were able to successfully demonstrate the Redis Transaction with Spring Boot for executing multiple operations as a single unit of work.
Learn more about Redis with Spring Boot.
The source code is available here.
Happy learning 🙂

